Meta Drops 405B Parameter Groundbreaking AI Language Model
Unveiling Llama 3.1 405B: Meta’s Groundbreaking AI Language Model
Llama 3.1 model
In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence, Meta has made a significant splash with the release of its latest language model, Llama 3.1 405B.
With a staggering 405 billion parameters, this model not only pushes the boundaries of what open-source AI can achieve but also positions itself as a formidable competitor to proprietary models from industry giants like OpenAI and Anthropic.
In this review, we will explore the advanced capabilities, training processes, availability, and the ongoing debate surrounding its licensing, providing a comprehensive overview of this groundbreaking development.
Advanced Capabilities and Specifications
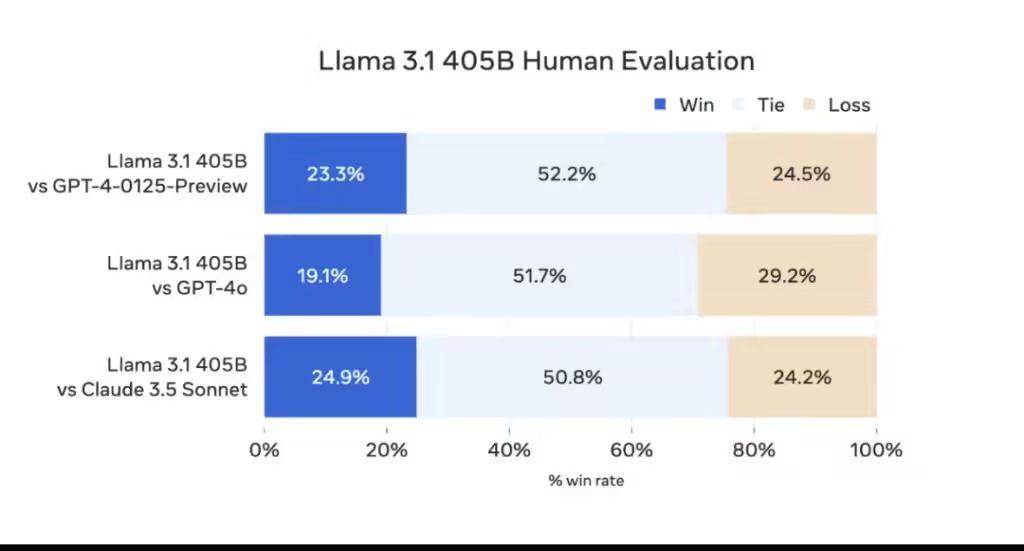
The Llama 3.1 405B model is designed to excel across a wide range of tasks, showcasing advanced capabilities in general knowledge, long-form text generation, multilingual translation, coding, mathematics, and complex reasoning.
One of the standout features of this model is its impressive 128K token context window, which is a remarkable 16-fold increase compared to its predecessor.
This allows for better contextual understanding and more coherent outputs, particularly in lengthy interactions.
Benchmarks indicate that Llama 3.1 405B outperforms its competitors in several areas.
For instance, it has shown superior performance in tests such as GSM8K and Hellaswag, while slightly trailing behind in HumanEval and MMLU-social sciences.
These enhancements not only make it a powerful tool for synthetic data generation and model distillation but also open new avenues for research and development in AI.
Training and Availability
Training such a colossal model required immense computational resources. Meta utilized over 16,000 NVIDIA H100 GPUs to process more than 15 trillion tokens, a feat that underscores the scale and ambition of this project.
The Llama 3.1 405B model, along with its smaller 8B and 70B variants, is now available for developers and researchers to explore.
It can be downloaded from Hugging Face and accessed through major cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Additionally, users can experiment with the models via Meta’s AI chatbot, making it accessible to a broader audience.
Licensing and the Open-Source Debate

Despite its classification as “open-source,” the licensing terms for Llama 3.1 405B have ignited discussions within the AI community.
Critics, including Open Source Initiative executive director Stefano Maffulli, have pointed out that the model’s license contains restrictions that could limit its true open-source nature.
Concerns have been raised about the lack of transparency regarding the training datasets and usage instructions, which could pose risks for developers looking to implement the model in their projects.
Industry analyst Stephen O’Grady has also highlighted that the licensing prohibits usage by certain large companies, which contradicts the principles of open-source software.
In contrast, Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg has emphasized the importance of open-source AI development, framing it as a vital path forward for innovation and competition in the AI landscape.
Conclusion
The release of Llama 3.1 405B marks a pivotal moment in the field of artificial intelligence, showcasing Meta’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of open-source technology.
With its advanced capabilities, extensive training, and broad availability, this model is poised to make a significant impact on AI research and application.
However, the ongoing debate surrounding its licensing raises important questions about the future of open-source AI and the balance between innovation and accessibility.
As the AI landscape continues to evolve, Llama 3.1 405B will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of language models and their applications across various industries.









